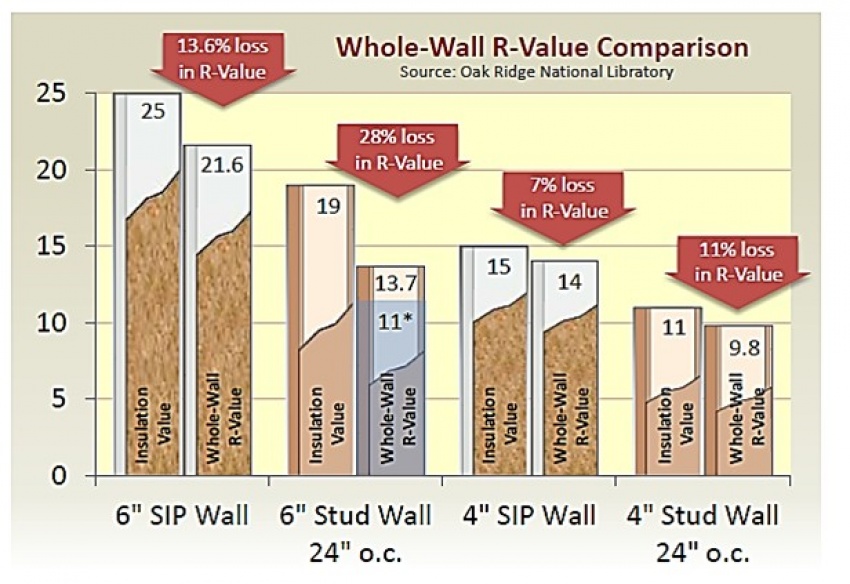
High R-Value Roofing Materials: Energy Efficiency and Comfort
High R-value roofing materials are a game-changer for homeowners seeking to improve energy efficiency and enhance indoor comfort. These materials, characterized by their exceptional ability to resist heat flow, play a pivotal role in reducing energy consumption and creating a more sustainable living environment. By understanding the principles of R-value and exploring the diverse range of high R-value roofing options available, homeowners can make informed decisions that optimize their home’s thermal performance and contribute to a greener future.
The R-value of a roofing material directly impacts its ability to insulate against heat transfer. A higher R-value signifies greater resistance to heat flow, meaning less heat escapes in the winter and less heat enters in the summer. This translates into significant energy savings on heating and cooling costs, making high R-value roofing a wise investment for both homeowners and the environment.
Understanding R-Value in Roofing
R-value is a measure of thermal resistance, indicating a material’s ability to resist heat flow. In roofing, R-value is crucial for energy efficiency and thermal comfort within a building. A higher R-value signifies greater resistance to heat transfer, meaning less heat escapes in winter and less heat enters in summer.
Impact of R-Value on Energy Efficiency and Thermal Performance
R-value directly affects a building’s energy efficiency and thermal performance. A roof with a higher R-value provides better insulation, minimizing heat loss during cold weather and heat gain during hot weather. This translates to lower heating and cooling costs for homeowners.
The Effect of R-Value on Heating and Cooling Costs
R-value plays a significant role in determining heating and cooling costs. A roof with a high R-value acts as a barrier, preventing heat from escaping during winter and reducing the need for excessive heating. Similarly, in summer, a high R-value roof minimizes heat gain, reducing reliance on air conditioning.
For instance, a home with a roof having an R-value of 30 might require 15% less energy for heating and cooling compared to a home with an R-value of 15.
High R-Value Roofing Materials
Choosing roofing materials with high R-values is crucial for energy efficiency and reducing heating and cooling costs. R-value, which stands for thermal resistance, measures a material’s ability to resist heat flow. A higher R-value indicates better insulation, preventing heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. This section explores common roofing materials with high R-values, comparing their thermal performance and highlighting their advantages and disadvantages.
Common High R-Value Roofing Materials
The thermal performance of roofing materials varies depending on the material itself and its installation method. Common roofing materials with high R-values include:
- Insulated Metal Panels: These panels combine a metal exterior with a core of rigid foam insulation. Their high R-values, typically ranging from R-10 to R-30, make them highly effective in reducing heat transfer.
- Spray Foam Insulation: Applied directly to the roof deck, spray foam insulation offers excellent thermal performance with R-values ranging from R-3 to R-7 per inch of thickness.
- Fiberglass Batts: Fiberglass batts are commonly used in attics and are available in various thicknesses. They provide a cost-effective solution with R-values ranging from R-13 to R-38.
- Cellular PVC Roofing: Cellular PVC roofing is a lightweight and durable option that provides excellent thermal performance with R-values ranging from R-5 to R-8 per inch.
- Polyisocyanurate (Polyiso) Foam Boards: Polyiso foam boards offer high R-values, typically ranging from R-5 to R-8 per inch, making them a popular choice for roofing insulation.
Thermal Performance Comparison
The table below compares the thermal performance of different high R-value roofing materials:
| Material | R-Value (per inch) | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insulated Metal Panels | R-10 to R-30 | High R-value, durable, aesthetically pleasing | Higher initial cost, potential for condensation issues |
| Spray Foam Insulation | R-3 to R-7 | Excellent thermal performance, air sealing, reduces noise | Can be expensive, requires professional installation |
| Fiberglass Batts | R-13 to R-38 | Cost-effective, easy to install | Lower R-value than other options, potential for settling |
| Cellular PVC Roofing | R-5 to R-8 | Lightweight, durable, resists moisture | Higher cost than traditional roofing materials |
| Polyiso Foam Boards | R-5 to R-8 | High R-value, moisture-resistant, easy to install | Potential for thermal bridging if not installed properly |
Advantages of High R-Value Roofing Materials
High R-value roofing materials offer several advantages, including:
- Energy Savings: They reduce heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, resulting in lower heating and cooling costs.
- Increased Comfort: They create a more comfortable living environment by maintaining a stable indoor temperature.
- Reduced Environmental Impact: They minimize energy consumption, reducing carbon emissions and promoting sustainability.
Disadvantages of High R-Value Roofing Materials
While offering numerous benefits, high R-value roofing materials also have some disadvantages:
- Higher Initial Cost: They generally have a higher initial cost compared to traditional roofing materials.
- Installation Complexity: Some materials, like spray foam insulation, require professional installation.
- Potential for Moisture Issues: Certain materials, like insulated metal panels, can trap moisture if not installed properly.
Factors Influencing R-Value in Roofing
The R-value of roofing materials is not a fixed characteristic but rather a dynamic property influenced by several factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed decisions about roofing insulation and achieving optimal thermal performance.
Insulation Thickness
Insulation thickness is directly proportional to R-value. This means that thicker insulation provides greater resistance to heat flow. The relationship between thickness and R-value is typically linear for most common insulation materials. For example, doubling the thickness of fiberglass insulation generally doubles its R-value.
The R-value of insulation is directly proportional to its thickness.
This principle is fundamental to maximizing the thermal performance of a roof. Choosing insulation with sufficient thickness is essential for achieving the desired R-value and ensuring effective heat resistance.
Air Gaps and Ventilation
Air gaps and ventilation play a critical role in thermal performance by influencing the movement of heat within the roof assembly. Air gaps can act as insulation, reducing heat transfer, while ventilation helps remove moisture and prevent condensation.
- Air Gaps: Air gaps can be intentionally created within the roof structure to enhance insulation. For instance, a space between the roof sheathing and the insulation layer can create an air gap, reducing heat transfer.
- Ventilation: Proper ventilation helps remove moisture and heat buildup within the attic space. This reduces the risk of condensation, which can lead to mold growth and damage. Ventilation is typically achieved through vents in the soffits and ridge of the roof.
Installation Techniques
Proper installation techniques are essential for maximizing the R-value of roofing materials. Even the best insulation materials will perform poorly if installed incorrectly.
- Continuous Insulation: Continuous insulation refers to the installation of insulation without breaks or gaps. This ensures a consistent thermal barrier across the entire roof surface.
- Air Sealing: Air sealing is crucial for preventing air leakage, which can significantly reduce the effectiveness of insulation. This involves sealing gaps and cracks around windows, doors, and other openings.
- Moisture Control: Moisture can compromise the performance of insulation. Proper moisture control measures, such as vapor barriers, are essential to prevent moisture buildup within the roof assembly.
Benefits of High R-Value Roofing
Investing in high R-value roofing offers a multitude of benefits that extend beyond simply improving energy efficiency. These benefits translate into tangible savings, a more sustainable lifestyle, and a more comfortable living environment.
Energy Savings
High R-value roofing significantly reduces the amount of heat lost during winter and gained during summer, leading to substantial energy savings. This is achieved through the insulation properties of the roofing material, which acts as a barrier against heat transfer. The higher the R-value, the better the insulation, resulting in less energy required to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
For example, a home with an R-value of 30 in the attic can reduce heating and cooling costs by up to 20% compared to a home with an R-value of 19.
Environmental Benefits
Reducing energy consumption through high R-value roofing has a positive impact on the environment. By decreasing reliance on fossil fuels for heating and cooling, you contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change.
According to the Environmental Protection Agency, the average American household spends about $2,200 annually on energy bills, a significant portion of which is used for heating and cooling. By improving insulation through high R-value roofing, homeowners can significantly reduce their carbon footprint.
Enhanced Indoor Comfort
High R-value roofing helps create a more comfortable indoor environment by maintaining a stable temperature year-round. This means warmer winters and cooler summers, eliminating the need for extreme temperature adjustments. The consistent temperature also reduces the risk of drafts and uneven heating or cooling, contributing to a more pleasant living experience.
Considerations for High R-Value Roofing
While high R-value roofing offers numerous benefits, it’s crucial to consider several factors before making a decision. These factors can significantly influence the overall cost, feasibility, and effectiveness of your roofing system.
Cost Implications of High R-Value Roofing
High R-value roofing materials generally cost more than conventional options. This increased cost is attributed to the advanced insulation properties, specialized manufacturing processes, and often, the heavier weight of these materials.
- Material Cost: High R-value materials like spray foam, rigid foam boards, or certain types of asphalt shingles are typically more expensive than traditional materials like asphalt shingles with fiberglass mats.
- Installation Cost: Installing high R-value roofing often requires specialized expertise and equipment, leading to higher labor costs. For example, spray foam insulation requires trained technicians and specialized equipment, which can increase installation costs.
- Structural Considerations: The added weight of high R-value materials might necessitate reinforcing the existing roof structure, leading to additional costs for structural engineering and reinforcement work.
Challenges and Limitations of High R-Value Roofing
While high R-value roofing offers significant advantages, it’s important to be aware of potential challenges and limitations.
- Weight: High R-value materials, particularly those with dense insulation, can be significantly heavier than traditional roofing materials. This weight can put stress on the existing roof structure, requiring structural evaluations and potentially costly reinforcement.
- Moisture Management: Maintaining a dry roof system is crucial for the long-term performance of any roofing material, especially high R-value options. Moisture can compromise the insulation’s effectiveness and lead to mold growth. Proper ventilation and moisture barriers are essential to prevent moisture buildup.
- Installation Complexity: Installing some high R-value materials, like spray foam or complex assemblies, requires specialized expertise and meticulous attention to detail. Improper installation can compromise the insulation’s effectiveness and potentially lead to future problems.
Choosing the Appropriate High R-Value Roofing Material
Selecting the right high R-value roofing material depends on several factors, including your budget, climate, roof structure, and aesthetic preferences.
- Climate: In regions with extreme temperatures, high R-value materials can significantly reduce heating and cooling costs. For example, in cold climates, a high R-value roof can help retain heat, reducing energy consumption.
- Roof Structure: The existing roof structure’s capacity to support the added weight of high R-value materials should be carefully considered. Structural engineers can assess the roof’s load-bearing capacity and recommend appropriate reinforcement if needed.
- Budget: High R-value roofing materials come in a range of price points. It’s essential to balance the potential energy savings with the initial investment cost.
Recommendation: Consult with a qualified roofing contractor and a structural engineer to determine the most suitable high R-value roofing material for your specific needs and budget.
Case Studies and Examples
Real-world applications of high R-value roofing demonstrate its effectiveness in reducing energy consumption and improving building comfort. This section explores specific examples and analyzes their impact on energy bills, comfort levels, and long-term performance.
Energy Savings and Comfort Improvements
High R-value roofing significantly reduces heat transfer through the roof, resulting in substantial energy savings and improved indoor comfort.
- A study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) found that a home with a high R-value roof (R-49) could save up to 20% on heating and cooling costs compared to a home with a standard R-value roof (R-30).
- In a commercial building with a large roof area, high R-value roofing can significantly reduce the load on the HVAC system, leading to lower energy consumption and reduced operating costs. For example, a 10,000 square foot office building with a high R-value roof could see a reduction in cooling costs of up to 30% compared to a building with a standard R-value roof.
Long-Term Performance and Sustainability
High R-value roofing materials are designed for durability and longevity, offering long-term performance and sustainability benefits.
- Many high R-value roofing materials, such as spray foam insulation and rigid foam insulation boards, are highly resistant to moisture and decay, ensuring their long-term performance and minimizing maintenance requirements.
- These materials also contribute to a building’s overall sustainability by reducing energy consumption and minimizing the environmental impact of heating and cooling systems.
Examples of Buildings with High R-Value Roofing
Numerous buildings around the world showcase the benefits of high R-value roofing.
- The LEED-certified GreenPix Zero Energy Media Center in California features a high R-value roof that contributes to the building’s energy efficiency and sustainability goals.
- The University of California, Berkeley’s new student housing complex utilizes high R-value roofing to reduce energy consumption and provide a comfortable living environment for students.
- The Seattle Public Library, a landmark building in the city, incorporates high R-value roofing to minimize heat gain and maintain a comfortable indoor environment.
Impact on Energy Bills and Comfort Levels
High R-value roofing directly impacts energy bills and indoor comfort by reducing heat transfer through the roof.
- Homes and buildings with high R-value roofing experience lower heating and cooling costs due to reduced energy consumption. This can result in significant cost savings over the long term.
- The reduced heat transfer also contributes to a more comfortable indoor environment, with less fluctuation in temperature throughout the year. This can lead to improved occupant satisfaction and productivity.
Concluding Remarks
Investing in high R-value roofing is a smart decision that pays dividends in terms of energy efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced indoor comfort. By carefully considering the factors influencing R-value, such as insulation thickness, air gaps, and proper installation techniques, homeowners can optimize their roofing system for optimal thermal performance. From reducing energy consumption and lowering utility bills to creating a more comfortable and sustainable living space, high R-value roofing offers a compelling solution for those seeking to build a greener and more energy-efficient home.