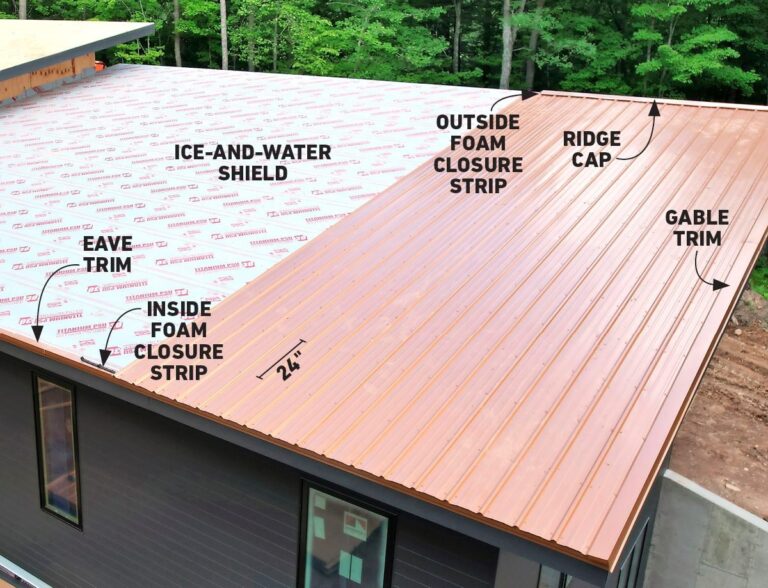
Heat-Resistant Roof Coatings: Protecting Buildings from the Sun
Heat-resistant roof coatings offer a practical and effective solution to the growing challenge of rising roof temperatures, especially in urban areas and regions with intense sunlight. These specialized coatings act as a protective barrier, reflecting solar radiation and reducing heat absorption, ultimately lowering the internal temperature of buildings and minimizing energy consumption.
The benefits of heat-resistant roof coatings extend beyond temperature regulation. They also contribute to increased energy efficiency, reduced cooling costs, and a more sustainable built environment. By mitigating the urban heat island effect, these coatings help create cooler and more comfortable cities, enhancing the overall quality of life for residents.
Introduction to Heat-Resistant Roof Coatings
Heat-resistant roof coatings are specially formulated materials designed to reflect solar radiation and reduce heat absorption, ultimately lowering the temperature of a building’s roof. These coatings offer a range of benefits, including energy savings, extended roof lifespan, and improved indoor comfort.
High roof temperatures pose significant challenges for building owners and occupants. Excessive heat can lead to increased energy consumption for cooling, premature roof deterioration, and even health risks for individuals working or residing in the building.
Buildings Requiring Heat-Resistant Roof Coatings
Buildings that are particularly susceptible to high roof temperatures and benefit from heat-resistant coatings include:
- Commercial buildings with large flat roofs, such as warehouses, factories, and retail stores.
- Residential homes located in hot climates or with dark-colored roofs.
- Agricultural structures, like barns and greenhouses, which are often exposed to intense sunlight.
- Public buildings, such as schools, hospitals, and government offices, where indoor comfort and energy efficiency are crucial.
Types of Heat-Resistant Roof Coatings
Heat-resistant roof coatings are essential for protecting buildings from the damaging effects of high temperatures. They are designed to reflect solar radiation, reduce heat absorption, and extend the lifespan of roofs. These coatings are available in various formulations, each with unique properties, advantages, and disadvantages. Understanding the different types of heat-resistant roof coatings is crucial for choosing the best option for a particular application.
Acrylic Roof Coatings
Acrylic roof coatings are a popular choice for heat-resistant applications due to their affordability and ease of application. They are water-based, making them environmentally friendly and low-odor. Acrylic coatings form a durable, flexible membrane that can withstand temperature fluctuations.
- Advantages:
- Affordable
- Easy to apply
- Water-based, making them environmentally friendly
- Durable and flexible
- Can be used on various roof surfaces
- Disadvantages:
- Lower heat reflectivity compared to other types
- May require more frequent reapplication
- Susceptible to UV degradation
- Applications:
- Residential and commercial buildings
- Roofs with moderate heat exposure
Silicone Roof Coatings
Silicone roof coatings are known for their exceptional heat resistance and longevity. They are highly reflective, effectively reducing heat absorption and lowering roof temperatures. Silicone coatings are also resistant to moisture, making them suitable for areas with high humidity.
- Advantages:
- High heat reflectivity
- Excellent moisture resistance
- Long lifespan
- Can be applied over various substrates
- Disadvantages:
- More expensive than acrylic coatings
- May require specialized application techniques
- Applications:
- Industrial and commercial buildings
- Roofs with high heat exposure
- Coastal areas with high humidity
Polyurethane Roof Coatings
Polyurethane roof coatings offer excellent adhesion, durability, and waterproofing properties. They are commonly used for both new and existing roofs, providing a protective barrier against the elements. Polyurethane coatings are also available in various colors, allowing for aesthetic customization.
- Advantages:
- Excellent adhesion
- Durable and long-lasting
- Waterproofing properties
- Available in various colors
- Disadvantages:
- Less heat reflective than silicone coatings
- May require professional application
- Applications:
- Residential and commercial buildings
- Roofs with moderate to high heat exposure
- Flat and sloped roofs
Application and Installation of Heat-Resistant Roof Coatings
Applying heat-resistant roof coatings is a process that requires careful preparation and meticulous execution to ensure optimal performance and longevity. The application process typically involves several steps, each crucial for achieving a durable and effective coating.
Surface Preparation and Treatment
Prior to applying the heat-resistant coating, the roof surface needs thorough preparation to ensure proper adhesion and longevity of the coating. This involves several steps:
- Cleaning: The roof surface must be cleaned to remove dirt, debris, loose particles, and any existing coatings that may hinder adhesion. A pressure washer can be used for effective cleaning, ensuring proper safety precautions are taken.
- Repairing: Any cracks, holes, or damaged areas on the roof surface should be repaired using appropriate materials like patching compounds or sealants. This step ensures a smooth and even surface for coating application.
- Priming: Applying a primer specifically designed for heat-resistant coatings is crucial. Primers improve adhesion, promote better bonding, and enhance the coating’s overall performance.
Tools and Equipment
The application of heat-resistant roof coatings requires specific tools and equipment for efficient and accurate application. The following are essential tools:
- Roller: A long-handled roller is ideal for applying the coating evenly across large areas of the roof surface.
- Brush: A brush is necessary for applying the coating in hard-to-reach areas and corners of the roof.
- Sprayer: For large-scale projects, a sprayer can be used for faster and more efficient application.
- Protective Gear: It is essential to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) during application, including gloves, masks, and safety goggles, to protect from potential hazards.
Application Process
The application of heat-resistant roof coatings involves a specific process to ensure proper coverage and effectiveness:
- Mixing: Carefully mix the coating according to the manufacturer’s instructions, ensuring a uniform consistency.
- Application: Apply the coating in thin, even layers, allowing each layer to dry completely before applying the next. This ensures proper coverage and prevents the coating from becoming too thick.
- Drying Time: Allow the coating to dry completely according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. The drying time may vary depending on factors such as temperature, humidity, and coating thickness.
- Inspection: After the coating has dried, inspect the roof surface for any imperfections or areas that may require additional application.
Performance and Durability of Heat-Resistant Roof Coatings
The performance and durability of heat-resistant roof coatings are crucial factors to consider when selecting a coating for your building. These coatings are designed to withstand extreme temperatures and harsh weather conditions, protecting your roof from damage and extending its lifespan. The effectiveness of these coatings depends on various factors, including the type of coating, the application process, and the environmental conditions they are exposed to.
Factors Influencing Performance and Durability
The performance and durability of heat-resistant roof coatings are influenced by several factors, including:
- Type of coating: Different types of heat-resistant coatings have varying properties, such as thermal conductivity, UV resistance, and chemical resistance. Choosing the right type of coating for your specific needs is essential.
- Application process: Proper application techniques, such as surface preparation, coating thickness, and curing time, are critical for ensuring the coating’s performance and durability. Improper application can lead to premature failure and reduce the coating’s effectiveness.
- Environmental conditions: Exposure to UV radiation, temperature fluctuations, and moisture can degrade the coating over time. Coatings with higher UV resistance and moisture resistance will perform better in harsh environments.
- Maintenance and upkeep: Regular maintenance, such as cleaning and inspection, can help to extend the lifespan of the coating. Early detection and repair of any damage can prevent further deterioration and ensure the coating’s continued effectiveness.
Impact of Environmental Factors
Environmental factors play a significant role in the performance and durability of heat-resistant roof coatings. Exposure to UV radiation can cause the coating to degrade, leading to fading, cracking, and chalking. Temperature fluctuations can also cause the coating to expand and contract, potentially leading to cracking and delamination. Moisture can penetrate the coating, leading to corrosion and mildew growth.
- UV exposure: UV radiation can break down the chemical bonds in the coating, leading to fading, cracking, and chalking. Coatings with high UV resistance are essential for areas with prolonged sun exposure. For example, a roof coating with a high UV resistance rating of 50+ will provide better protection against UV damage than a coating with a lower rating.
- Temperature fluctuations: Extreme temperature fluctuations can cause the coating to expand and contract, potentially leading to cracking and delamination. Coatings with high flexibility and thermal stability are better suited for areas with significant temperature variations. A good example is a roof coating formulated with a high-performance elastomeric polymer, which can withstand significant temperature changes without cracking or delaminating.
- Moisture: Moisture can penetrate the coating, leading to corrosion and mildew growth. Coatings with high moisture resistance are essential for areas with high humidity or frequent rainfall. A coating with a water-repellent property will prevent moisture from penetrating the coating and damaging the underlying roof structure.
Best Practices for Maintenance and Upkeep
Regular maintenance and upkeep are essential for extending the lifespan of heat-resistant roof coatings. Here are some best practices:
- Regular inspection: Inspect the coating regularly for any signs of damage, such as cracking, peeling, or fading. Early detection and repair of any damage can prevent further deterioration and ensure the coating’s continued effectiveness.
- Cleaning: Clean the coating regularly to remove dirt, debris, and algae. A gentle cleaning solution and a soft brush can be used to remove dirt and debris without damaging the coating. Regular cleaning will prevent dirt and debris from accumulating and damaging the coating.
- Re-coating: Re-coat the roof as needed to maintain its effectiveness. The frequency of re-coating will depend on the type of coating, the environmental conditions, and the level of wear and tear. Following the manufacturer’s recommendations for re-coating will ensure the coating’s continued effectiveness.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Benefits
Heat-resistant roof coatings offer significant advantages in terms of energy efficiency and environmental sustainability, particularly in regions experiencing extreme temperatures. These coatings play a crucial role in reducing energy consumption and mitigating the adverse effects of urban heat islands.
Energy Savings and Cost Reductions
Heat-resistant roof coatings contribute to energy efficiency by reflecting solar radiation, reducing the amount of heat absorbed by the roof surface. This minimizes the heat transfer into the building, lowering the demand for cooling systems and reducing energy consumption.
The potential energy savings associated with heat-resistant roof coatings can be substantial. Studies have shown that these coatings can reduce cooling energy consumption by up to 20%, translating into significant cost reductions for building owners. For example, a commercial building with a 10,000 square foot roof could achieve annual energy savings of up to $2,000 by using a heat-resistant roof coating.
Environmental Benefits
Heat-resistant roof coatings contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing the heat island effect, a phenomenon where urban areas experience higher temperatures than surrounding rural areas. This effect is primarily caused by the absorption of solar radiation by dark surfaces like asphalt and concrete.
- Heat-resistant roof coatings reflect a significant portion of solar radiation, reducing the amount of heat absorbed by the roof surface. This helps mitigate the heat island effect, lowering ambient temperatures in urban areas.
- By reducing the demand for air conditioning, heat-resistant roof coatings contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions, as air conditioners are major contributors to energy consumption and carbon footprint.
Safety Considerations
While heat-resistant roof coatings offer numerous benefits, it’s crucial to prioritize safety during their application and use. Proper precautions are essential to minimize risks and ensure a safe working environment.
Potential Hazards
The application and use of heat-resistant roof coatings can pose various hazards, including:
- Exposure to Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Many heat-resistant coatings contain VOCs, which can be harmful if inhaled. Long-term exposure can lead to respiratory problems, headaches, and dizziness.
- Skin and Eye Irritation: Some coating components can irritate the skin and eyes. Direct contact can cause redness, itching, and burning sensations.
- Fire Hazards: Heat-resistant coatings are often flammable, especially during application. Improper handling or storage can lead to fire hazards.
- Falls from Heights: Roof work inherently involves working at heights, which increases the risk of falls. Proper safety measures are essential to prevent accidents.
- Exposure to Hazardous Materials: Some coatings contain heavy metals or other hazardous materials that can be harmful if ingested or absorbed through the skin.
Safety Measures and Protective Equipment
To mitigate these hazards, it’s crucial to follow recommended safety measures and wear appropriate protective equipment:
- Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation during application and drying to minimize VOC exposure. Use fans or other ventilation systems to remove fumes from the work area.
- Respiratory Protection: Wear a NIOSH-approved respirator to protect against VOCs and other airborne particles. The type of respirator will depend on the specific coating and its VOC content.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety goggles or a face shield to protect your eyes from splashes or airborne particles.
- Skin Protection: Wear gloves made of nitrile or other suitable material to prevent skin contact with the coating. Long sleeves and pants are also recommended.
- Fall Protection: Use safety harnesses, lifelines, and other fall protection equipment when working at heights. Ensure proper installation and inspection of all equipment.
- Fire Safety: Keep a fire extinguisher readily available in the work area. Follow manufacturer instructions for safe handling and storage of flammable materials.
Handling and Disposal of Coating Materials
Proper handling and disposal of coating materials are crucial to minimize environmental impact and protect human health.
- Storage: Store coating materials in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from heat sources and direct sunlight. Follow manufacturer recommendations for storage temperatures and conditions.
- Spill Response: In case of spills, immediately contain the spill using absorbent materials and dispose of them properly. Avoid contact with the spilled material.
- Disposal: Dispose of leftover coating materials according to local regulations and environmental guidelines. Contact your local waste management agency for proper disposal procedures.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Heat-resistant roof coatings have proven their effectiveness in various real-world applications, demonstrating their ability to reduce energy consumption, enhance building durability, and contribute to a more sustainable environment. Here are some compelling case studies that illustrate the tangible benefits of these coatings.
Successful Applications of Heat-Resistant Roof Coatings
Heat-resistant roof coatings have been successfully implemented in a wide range of projects, including:
- Commercial Buildings: A large office building in Phoenix, Arizona, experienced significant energy savings after applying a heat-resistant roof coating. The coating reflected solar radiation, reducing the building’s cooling load by 20% and lowering energy consumption. The building’s occupants also reported a noticeable improvement in indoor comfort due to the reduced heat gain.
- Industrial Facilities: A manufacturing plant in Houston, Texas, installed a heat-resistant roof coating to mitigate the effects of extreme temperatures. The coating’s high reflectivity significantly reduced the roof’s temperature, minimizing the risk of premature roof failure and extending the roof’s lifespan. The plant also saw a reduction in HVAC costs due to the improved thermal performance.
- Residential Homes: A homeowner in Miami, Florida, applied a heat-resistant roof coating to their home to reduce energy bills and improve indoor comfort. The coating’s high reflectivity and emissivity properties effectively reduced heat gain, resulting in lower air conditioning costs and a more comfortable living environment.
Impact of Heat-Resistant Roof Coatings
The impact of heat-resistant roof coatings can be measured in various ways, including:
- Energy Savings: By reflecting solar radiation and reducing heat gain, these coatings contribute to significant energy savings. Studies have shown that heat-resistant roof coatings can reduce cooling loads by up to 20%, leading to lower energy consumption and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
- Extended Roof Lifespan: The reflective properties of heat-resistant roof coatings protect the underlying roof membrane from the damaging effects of UV radiation and extreme temperatures, extending the roof’s lifespan and reducing the need for premature replacements.
- Improved Indoor Comfort: By reducing heat gain, these coatings create a more comfortable indoor environment, particularly in hot climates. This can improve employee productivity in commercial buildings and enhance the overall quality of life for residents.
Case Study Comparison
The following table compares different case studies, highlighting project details, coating type, and results:
| Project | Coating Type | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Office Building, Phoenix, AZ | Acrylic-based, high-reflective coating | 20% reduction in cooling load, lower energy consumption, improved indoor comfort. |
| Manufacturing Plant, Houston, TX | Silicone-based, heat-resistant coating | Reduced roof temperature, minimized risk of roof failure, extended roof lifespan, lower HVAC costs. |
| Residential Home, Miami, FL | Elastomeric, heat-reflecting coating | Lower air conditioning costs, improved indoor comfort, reduced energy consumption. |
Future Trends and Innovations
The field of heat-resistant roof coatings is continuously evolving, driven by the increasing demand for sustainable and energy-efficient building solutions. Advancements in material science, nanotechnology, and innovative manufacturing processes are paving the way for new and improved heat-resistant coatings with enhanced performance characteristics.
Advancements in Material Science
The development of novel materials is a key driver of innovation in heat-resistant roof coatings. Researchers are exploring advanced materials like aerogels, which possess exceptional thermal insulation properties due to their highly porous structure. Aerogels are lightweight, highly porous materials with a network of interconnected nanometer-sized pores, trapping air and reducing heat transfer. Their ability to reflect solar radiation and provide excellent thermal insulation makes them ideal for heat-resistant roof coatings.
Nanotechnology in Heat-Resistant Coatings
Nanotechnology is playing a crucial role in enhancing the performance of heat-resistant roof coatings. The use of nanoparticles in coating formulations can significantly improve their thermal reflectivity, durability, and longevity. For example, incorporating nanoparticles of titanium dioxide (TiO2) into the coating can enhance its ability to reflect infrared radiation, reducing heat absorption by the roof surface. These coatings can also be made self-cleaning by incorporating photocatalytic nanoparticles that break down dirt and grime when exposed to sunlight.
Smart Coatings for Adaptive Thermal Management
Smart coatings are emerging as a promising technology for adaptive thermal management of roofs. These coatings can respond to changes in environmental conditions, such as temperature and solar radiation, to adjust their thermal properties. For example, thermochromic coatings change color based on temperature, reflecting more solar radiation when hot and absorbing more when cold. This dynamic adaptation helps to regulate roof temperature and reduce energy consumption for cooling.
Bio-Based Coatings for Sustainability
There is a growing interest in developing bio-based heat-resistant roof coatings using renewable resources. These coatings can be derived from plant oils, polymers, and other natural materials, reducing reliance on petroleum-based products. Bio-based coatings can offer comparable performance to conventional coatings while contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly building sector.
Integration of Building Information Modeling (BIM)
The integration of Building Information Modeling (BIM) with heat-resistant roof coatings is enabling more efficient design, installation, and maintenance processes. BIM software allows architects and engineers to create virtual models of buildings, including roof systems, and simulate their performance under different conditions. This enables them to optimize the design of heat-resistant coatings for specific locations and climates, ensuring maximum energy efficiency and durability.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Several real-world examples demonstrate the effectiveness of advanced heat-resistant roof coatings. For instance, the use of aerogel-based coatings on commercial buildings in hot climates has resulted in significant reductions in cooling costs and improved indoor comfort. Similarly, the application of smart coatings on residential roofs has shown remarkable improvements in thermal regulation, reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, heat-resistant roof coatings represent a vital advancement in roofing technology, offering a comprehensive approach to managing heat gain and improving building performance. As concerns about climate change and energy consumption escalate, these coatings are poised to play an increasingly important role in shaping a more sustainable and resilient future for our built environment.