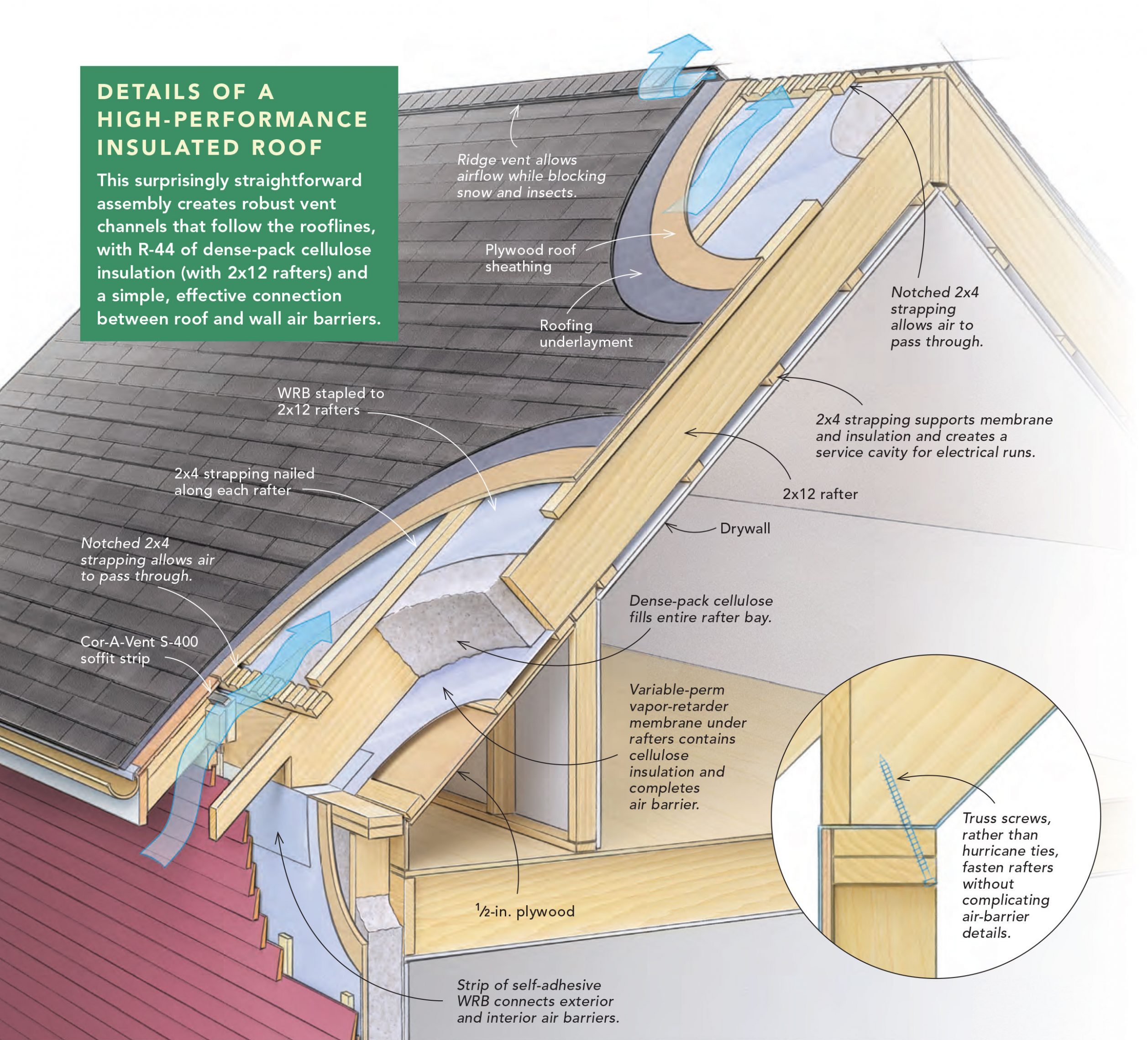
Roof Insulation Materials: A Guide to Energy Efficiency
Roof insulation materials play a crucial role in maximizing energy efficiency and comfort within a home. They act as a barrier, preventing heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer, creating a more comfortable living environment and significantly reducing energy bills.
Choosing the right insulation material depends on various factors, including climate, budget, and desired performance levels. This guide explores common insulation options, their pros and cons, installation considerations, and the impact they have on energy savings, comfort, and the environment.
Introduction to Roof Insulation Materials
A well-insulated roof is crucial for maintaining a comfortable and energy-efficient home. Roof insulation acts as a barrier, preventing heat from escaping during the winter and reducing heat gain during the summer. This helps maintain a consistent indoor temperature, enhancing comfort and reducing reliance on heating and cooling systems.
Benefits of Roof Insulation
Proper roof insulation offers a wide range of benefits, including:
- Reduced energy consumption: By preventing heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, roof insulation helps reduce the need for heating and cooling, leading to lower energy bills.
- Increased comfort: A well-insulated roof helps maintain a consistent indoor temperature, creating a more comfortable living environment throughout the year.
- Improved indoor air quality: Insulation can help prevent moisture buildup in the attic, reducing the risk of mold and mildew growth, which can negatively impact indoor air quality.
- Increased property value: Energy-efficient homes are more desirable to buyers, leading to increased property value.
- Reduced environmental impact: By reducing energy consumption, roof insulation contributes to a smaller carbon footprint.
Choosing the Right Insulation Material
Selecting the right insulation material is essential for achieving optimal performance and long-term benefits. The best choice depends on various factors, including:
- Climate: Different insulation materials offer varying levels of resistance to heat transfer, so the choice should be tailored to the local climate.
- Roof type: The type of roof construction, including the pitch and the presence of ventilation, influences the best insulation options.
- Budget: Insulation materials vary in cost, so it’s essential to consider the budget when making a decision.
- Sustainability: Some insulation materials are more environmentally friendly than others, so it’s important to consider sustainability factors.
Common Roof Insulation Materials
Choosing the right insulation material for your roof is crucial for maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature, reducing energy bills, and extending the lifespan of your roof. Several common roof insulation materials are available, each with its unique advantages and drawbacks. This section will delve into the characteristics, pros, cons, and applications of these materials.
Common Roof Insulation Materials
| Material | Pros | Cons | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiberglass Batts |
|
|
|
| Mineral Wool |
|
|
|
| Spray Foam |
|
|
|
| Cellulose |
|
|
|
| Rigid Foam Boards |
|
|
|
Factors to Consider When Choosing Roof Insulation Materials
Selecting the right roof insulation material is crucial for ensuring a comfortable and energy-efficient home. Several factors influence the choice of insulation, and understanding these factors is essential for making an informed decision.
Climate
The climate of your location plays a significant role in determining the type of insulation needed. In hot climates, insulation helps prevent heat gain, keeping your home cool. In cold climates, insulation helps prevent heat loss, keeping your home warm. For instance, in regions with extreme temperatures, a higher R-value insulation might be necessary compared to regions with milder climates.
R-Value
R-value is a measure of thermal resistance, indicating how well a material resists heat flow. Higher R-values signify better insulation performance. The R-value required for your roof depends on the climate and the desired level of energy efficiency. The recommended R-value for roofs varies by region and can be found on the U.S. Department of Energy website.
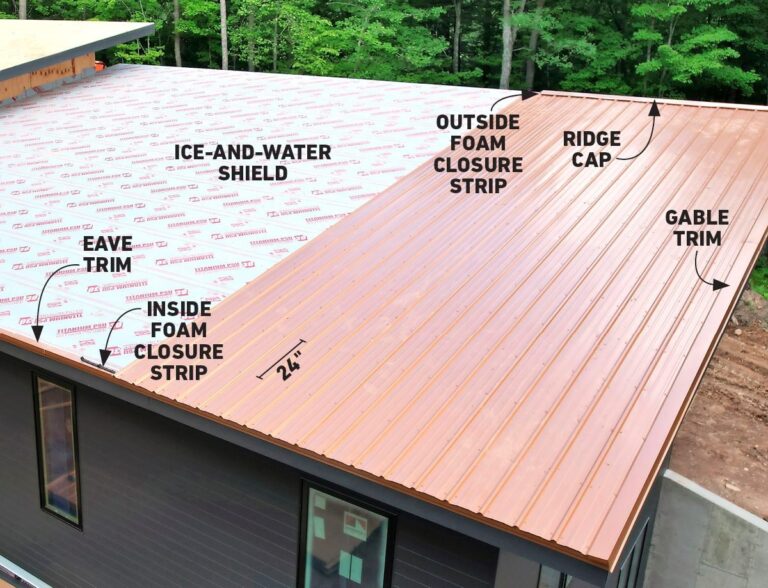
Installation Methods
Different insulation materials require different installation methods. Some materials, like fiberglass batts, are easy to install between joists, while others, like spray foam, require professional installation. The chosen installation method will also influence the overall cost of the insulation project.
Cost Considerations
The cost of roof insulation varies significantly depending on the material and installation method. Fiberglass batts are generally the most affordable option, while spray foam is more expensive. It is essential to consider the long-term savings on energy bills that insulation provides when comparing costs.
Checklist for Choosing Insulation
- Climate of your location
- Desired level of energy efficiency
- R-value requirements for your region
- Installation methods available
- Cost of materials and installation
- Environmental impact of the insulation material
- Fire resistance of the insulation material
- Moisture resistance of the insulation material
Installing Roof Insulation
Installing roof insulation is a crucial step in improving energy efficiency and reducing heating and cooling costs. Proper installation ensures optimal performance and longevity of the insulation.
Steps Involved in Installing Different Types of Roof Insulation
The installation process varies depending on the type of insulation used. Here’s a general overview:
- Batt Insulation: This type of insulation comes in rolls or batts and is typically installed between joists or rafters. It is usually held in place with staples or wire. Before installation, ensure the insulation is properly compressed to fit snugly in the space.
- Loose-Fill Insulation: This insulation, made of materials like cellulose or fiberglass, is blown into the attic space. It fills all gaps and crevices, creating a continuous barrier. Special equipment is required for installation, which involves blowing the insulation into the attic space using a specialized blower.
- Spray Foam Insulation: This insulation is applied as a liquid that expands and hardens to form a solid, continuous barrier. It is sprayed directly onto the underside of the roof deck, filling all gaps and crevices. This process requires specialized equipment and trained professionals.
- Rigid Foam Insulation: This type of insulation comes in boards and is typically installed on the underside of the roof deck or between rafters. It is usually attached with adhesive or mechanical fasteners.
Safety Precautions During Installation
Safety should always be prioritized during roof insulation installation:
- Wear appropriate safety gear: This includes gloves, eye protection, and a respirator to protect against dust and fibers. A hard hat is also crucial when working on the roof.
- Use a ladder safely: Always ensure the ladder is on a stable surface, properly secured, and extended far enough to reach the work area. Never overextend or climb beyond the top of the ladder.
- Be aware of electrical hazards: When working near power lines or electrical wiring, take extra precautions to avoid contact. Ensure all electrical circuits are disconnected before working in the area.
- Work with a partner: Having a partner on the roof for assistance and safety backup is highly recommended, especially when working at heights.
Tips for Achieving Optimal Insulation Performance
To maximize the effectiveness of roof insulation, follow these tips:
- Seal all air leaks: Air leaks can significantly reduce the effectiveness of insulation. Seal all gaps and cracks around windows, doors, and other openings in the roof. Use caulk, weather stripping, or spray foam sealant to achieve a tight seal.
- Maintain a continuous insulation layer: Ensure there are no gaps or breaks in the insulation layer. This is especially important for batt insulation, which should be carefully fitted and secured to prevent gaps.
- Consider the R-value: The R-value of insulation measures its resistance to heat flow. Higher R-values indicate better insulation performance. Choose an insulation material with an appropriate R-value for your climate and building code requirements.
Importance of Proper Ventilation in Conjunction with Roof Insulation
Proper ventilation is essential for maintaining a healthy attic space and maximizing the effectiveness of roof insulation.
- Prevent moisture buildup: Ventilation allows for the escape of moisture from the attic, preventing condensation and mold growth. It helps maintain a balanced humidity level, preventing damage to the roof structure and insulation.
- Improve insulation performance: Adequate ventilation helps regulate attic temperature, preventing heat buildup in the summer and heat loss in the winter. This improves the overall efficiency of the insulation system.
- Extend the life of the roof: A well-ventilated attic helps protect the roof from premature aging and deterioration caused by excessive heat and moisture.
Benefits of Roof Insulation
Roof insulation is a crucial component of a well-designed and energy-efficient home. By creating a barrier between the living space and the attic, roof insulation helps to regulate temperature, reduce energy consumption, and enhance overall comfort. This section explores the various benefits of roof insulation, highlighting its impact on energy efficiency, indoor comfort, cost savings, and environmental sustainability.
Energy Efficiency
Roof insulation plays a vital role in reducing energy consumption by preventing heat loss in the winter and heat gain in the summer. Properly insulated roofs minimize the amount of heat that escapes through the attic, reducing the need for heating and cooling systems to work harder.
- In winter, roof insulation acts as a barrier against cold air infiltrating the attic, preventing heat loss from the living space below. This helps maintain a comfortable indoor temperature while reducing heating costs.
- During the summer, roof insulation reflects solar heat away from the attic, minimizing heat gain. This reduces the strain on air conditioning systems, resulting in lower cooling costs and a more comfortable indoor environment.
Indoor Comfort
Roof insulation contributes significantly to indoor comfort by creating a more stable and comfortable living environment. By preventing temperature fluctuations, roof insulation helps to:
- Maintain a consistent indoor temperature throughout the year, reducing drafts and cold spots in the winter and hot spots in the summer.
- Reduce noise pollution from outside sources, creating a more peaceful and relaxing atmosphere.
- Improve air quality by reducing the amount of dust and allergens that can accumulate in the attic and filter down into the living space.
Cost Savings
Investing in proper roof insulation can lead to substantial cost savings over the long term. By reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling, roof insulation helps to:
- Lower monthly energy bills, providing a tangible return on investment.
- Extend the lifespan of heating and cooling systems by reducing the strain on these appliances.
- Increase the overall value of the property by making it more energy-efficient and desirable to potential buyers.
Environmental Benefits
Roof insulation promotes environmental sustainability by reducing energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. By lowering the reliance on fossil fuels for heating and cooling, roof insulation contributes to:
- A cleaner and healthier environment by reducing air pollution.
- A more sustainable future by reducing our carbon footprint and dependence on non-renewable energy sources.
- A more resilient and adaptable built environment, better equipped to withstand the effects of climate change.
Maintenance and Longevity of Roof Insulation
Roof insulation, like any other component of your home, requires proper maintenance to ensure its longevity and effectiveness. Understanding the lifespan of different insulation materials and implementing appropriate maintenance practices can significantly extend the life of your roof insulation, maximizing its energy-saving benefits and minimizing the need for costly replacements.
Lifespan of Roof Insulation Materials
The lifespan of roof insulation varies depending on the type of material used. Here’s a general overview of the expected lifespan for common insulation materials:
- Fiberglass Batts: Fiberglass batts typically last for 20-30 years, but their lifespan can be affected by factors such as moisture exposure and compaction.
- Blown-in Cellulose: Blown-in cellulose insulation has a lifespan of 50-75 years, making it a durable and long-lasting option. Its resistance to moisture and fire makes it an excellent choice for attic insulation.
- Spray Foam: Open-cell spray foam insulation can last for 20-30 years, while closed-cell spray foam can last for 50-75 years. Its excellent air-sealing properties and moisture resistance contribute to its long lifespan.
- Rigid Foam Boards: Rigid foam boards, like extruded polystyrene (XPS) and polyisocyanurate (polyiso), are known for their durability and can last for 50-75 years or more. Their resistance to moisture and fire makes them ideal for roofing applications.
Maintaining Roof Insulation
Regular maintenance is crucial for maximizing the lifespan and performance of your roof insulation. Here are some tips for maintaining your roof insulation:
- Regular Inspections: Conduct visual inspections of your attic space at least once a year, checking for signs of moisture, pests, or damage to the insulation. Early detection of problems allows for timely repairs, preventing further damage and ensuring the insulation’s effectiveness.
- Proper Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in your attic space to prevent moisture buildup, which can degrade insulation materials and create a breeding ground for mold and mildew. Proper ventilation helps maintain a balanced temperature and humidity level, promoting a healthy environment for your roof insulation.
- Moisture Control: Address any leaks or moisture sources in your roof or attic space promptly. Leaky pipes, condensation, or inadequate ventilation can lead to moisture buildup, damaging the insulation and compromising its effectiveness.
- Pest Control: Protect your insulation from pests like rodents, insects, and birds. Pests can damage insulation materials, creating gaps and compromising their effectiveness. Implement pest control measures to prevent infestations and maintain the integrity of your roof insulation.
Issues with Improper Installation or Maintenance
Improper installation or inadequate maintenance can lead to several issues with roof insulation, impacting its effectiveness and potentially causing damage to your home.
- Moisture Buildup: Insufficient ventilation or improper installation can lead to moisture buildup in the attic space, damaging the insulation and creating a breeding ground for mold and mildew. This can lead to health problems and structural damage to your home.
- Reduced Insulation Effectiveness: Moisture, compaction, or damage to the insulation can significantly reduce its R-value, compromising its thermal performance and increasing energy consumption.
- Pest Infestations: Gaps or openings in the insulation can attract pests, leading to infestations that damage the insulation, create unpleasant odors, and potentially spread diseases.
- Structural Damage: Moisture buildup, pest infestations, or improper installation can weaken the structural integrity of your roof and attic space, potentially leading to sagging, leaks, or even collapse.
Identifying and Addressing Problems with Roof Insulation
Several signs indicate potential problems with your roof insulation, requiring attention and corrective measures.
- High Energy Bills: Noticeably higher energy bills than usual, especially during the summer and winter months, can indicate insufficient or damaged insulation.
- Uneven Temperatures: If you experience significant temperature variations between different rooms in your home, particularly noticeable in the attic or upper floors, it might suggest inadequate insulation.
- Moisture or Mold: Signs of moisture or mold growth in your attic space, including condensation, dampness, or visible mold, indicate a potential moisture problem that could be affecting the insulation.
- Pests: Evidence of pest activity, such as droppings, gnawing, or nests, suggests a possible infestation that could be damaging your roof insulation.
- Visible Damage: Inspecting the attic space for visible damage to the insulation, such as tears, gaps, or compaction, can help identify areas requiring repair or replacement.
Sustainable Roof Insulation Options
Roof insulation plays a crucial role in energy efficiency and reducing environmental impact. Choosing sustainable insulation options is essential for minimizing the carbon footprint of your home and promoting a greener lifestyle.
Eco-Friendly Roof Insulation Materials
Sustainable roof insulation materials are designed to minimize environmental impact throughout their lifecycle, from production to disposal. These materials are often made from recycled or renewable resources, and they have low embodied energy, meaning they require less energy to manufacture.
- Cellulose Insulation: Made from recycled paper, cellulose insulation is a highly effective and sustainable option. It is naturally fire-resistant and provides excellent thermal insulation.
- Mineral Wool Insulation: Derived from rock or slag, mineral wool insulation is non-combustible and offers good thermal and acoustic insulation. It is also recyclable and has a low embodied energy.
- Sheep’s Wool Insulation: A natural and renewable material, sheep’s wool insulation provides excellent thermal and acoustic insulation. It is biodegradable and can be composted at the end of its life.
- Hemp Insulation: Hemp is a fast-growing and sustainable crop that can be used to create insulation. Hemp insulation is breathable, fire-resistant, and provides good thermal insulation.
- Aerogel Insulation: Aerogel insulation is a highly efficient material made from silica, a naturally occurring mineral. It is lightweight, non-toxic, and has excellent thermal insulation properties.
Environmental Impact of Insulation Choices
The environmental impact of insulation materials can be assessed by considering factors such as embodied energy, greenhouse gas emissions, and recyclability.
- Embodied Energy: The energy required to manufacture, transport, and install insulation materials. Materials with low embodied energy are more sustainable.
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Insulation materials can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions during production and disposal. Choosing materials with low emissions is crucial.
- Recyclability: Some insulation materials can be recycled at the end of their life, reducing waste and conserving resources.
Recycling and Disposal of Insulation Materials
Proper recycling and disposal of insulation materials are essential for minimizing environmental impact.
- Cellulose Insulation: Cellulose insulation can be recycled and reused in some cases. However, it is generally recommended to dispose of it in landfills.
- Mineral Wool Insulation: Mineral wool insulation is recyclable and can be reused in various applications.
- Sheep’s Wool Insulation: Sheep’s wool insulation is biodegradable and can be composted at the end of its life.
- Hemp Insulation: Hemp insulation is biodegradable and can be composted or recycled.
- Aerogel Insulation: Aerogel insulation is not currently recyclable, but research is ongoing to develop recycling methods.
Role of Sustainable Roof Insulation in Reducing Carbon Footprint
Sustainable roof insulation plays a significant role in reducing carbon footprint by improving energy efficiency and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
“By choosing sustainable roof insulation, homeowners can significantly reduce their energy consumption, lower their heating and cooling costs, and contribute to a greener future.”
Future Trends in Roof Insulation
The field of roof insulation is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in materials, installation techniques, and a growing focus on sustainability and energy efficiency. These innovations are shaping the future of roof insulation, leading to more effective, environmentally friendly, and cost-effective solutions.
Emerging Technologies and Innovations
The development of new materials and technologies is at the forefront of innovation in roof insulation.
- Aerogel Insulation: This highly porous material, composed of silica or other materials, offers exceptional thermal insulation properties while being lightweight and durable. Aerogel insulation can be incorporated into various roof systems, providing superior thermal resistance and energy savings.
- Vacuum Insulation Panels (VIPs): VIPs consist of a core material enclosed in a vacuum-sealed envelope. This technology creates a highly efficient insulating layer that significantly reduces heat transfer, making it ideal for roofs with limited space.
- Phase Change Materials (PCMs): PCMs absorb and release heat during temperature fluctuations, providing a buffer against extreme temperatures. These materials can be integrated into roof insulation systems, enhancing thermal comfort and reducing energy consumption.
- Spray Foam Insulation: Open-cell and closed-cell spray foam insulation are becoming increasingly popular due to their ability to create air-tight seals and conform to complex roof shapes. These materials offer superior insulation performance and can reduce air infiltration, leading to improved energy efficiency.
Impact of Advancements in Materials and Installation Techniques
Advancements in materials and installation techniques are transforming the way roof insulation is designed and implemented.
- Improved Thermal Performance: New materials, such as aerogel and VIPs, offer significantly higher thermal resistance compared to traditional insulation, leading to greater energy savings and reduced heating and cooling costs.
- Enhanced Durability and Longevity: Innovations in materials, such as spray foam and aerogel, contribute to improved durability and longevity, extending the lifespan of roof insulation systems and reducing maintenance requirements.
- Simplified Installation: Advanced installation techniques, such as spray foam application, streamline the installation process, making it faster and more efficient, while also minimizing disruptions to building occupants.
- Increased Accessibility: The development of thinner and lighter insulation materials, such as aerogel, makes it easier to insulate roofs with limited space, expanding the accessibility of high-performance insulation to a wider range of buildings.
Future of Sustainable and Energy-Efficient Roof Insulation
Sustainability and energy efficiency are driving the future of roof insulation, with a focus on reducing environmental impact and promoting energy conservation.
- Bio-Based Insulation Materials: The use of sustainable and renewable materials, such as hemp, cellulose, and recycled materials, is gaining traction in the insulation industry. These materials offer excellent thermal performance while reducing reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing environmental footprint.
- Integrated Roof Systems: The concept of integrated roof systems, combining insulation with other components like roofing membranes and solar panels, is gaining popularity. These systems optimize energy efficiency, reduce installation complexity, and enhance overall building performance.
- Smart Insulation Technologies: Emerging smart insulation technologies, such as self-healing materials and adaptive insulation systems, are being explored to further enhance energy efficiency and optimize thermal performance. These technologies are expected to play a crucial role in shaping the future of roof insulation.
Conclusion
Investing in proper roof insulation is a wise decision for any homeowner. It not only enhances comfort and reduces energy costs but also contributes to a greener footprint. By understanding the different insulation materials and their properties, you can make informed choices that benefit your home, wallet, and the planet.